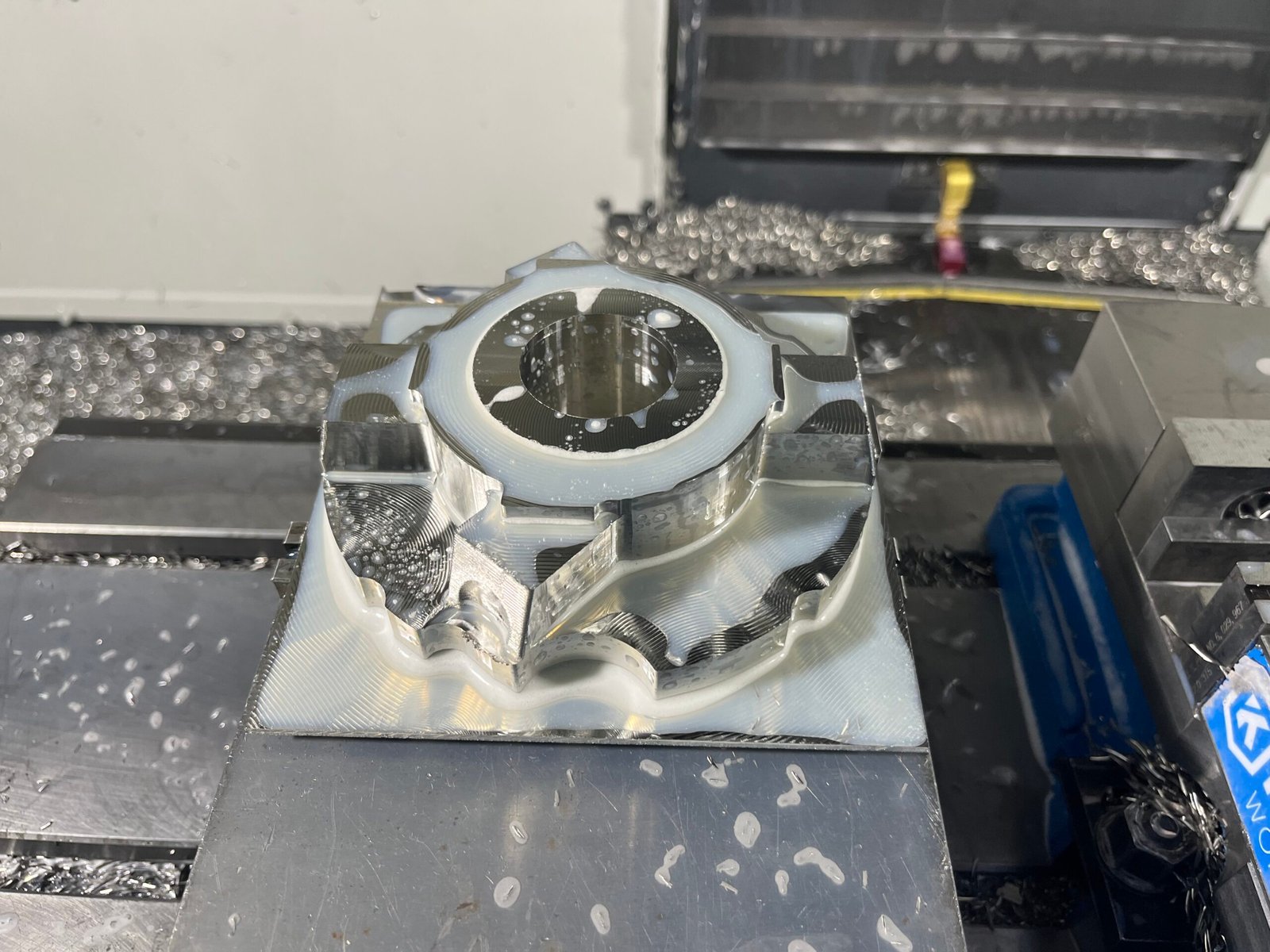
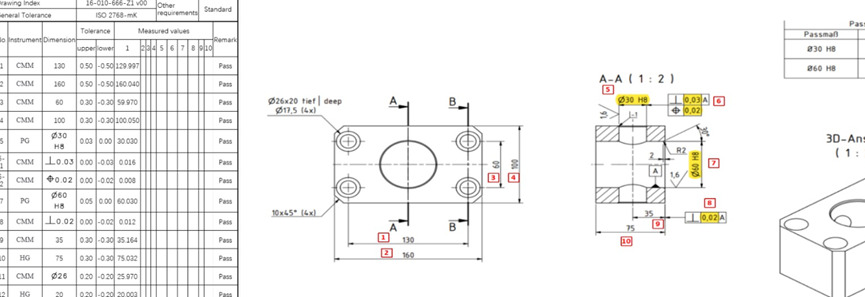
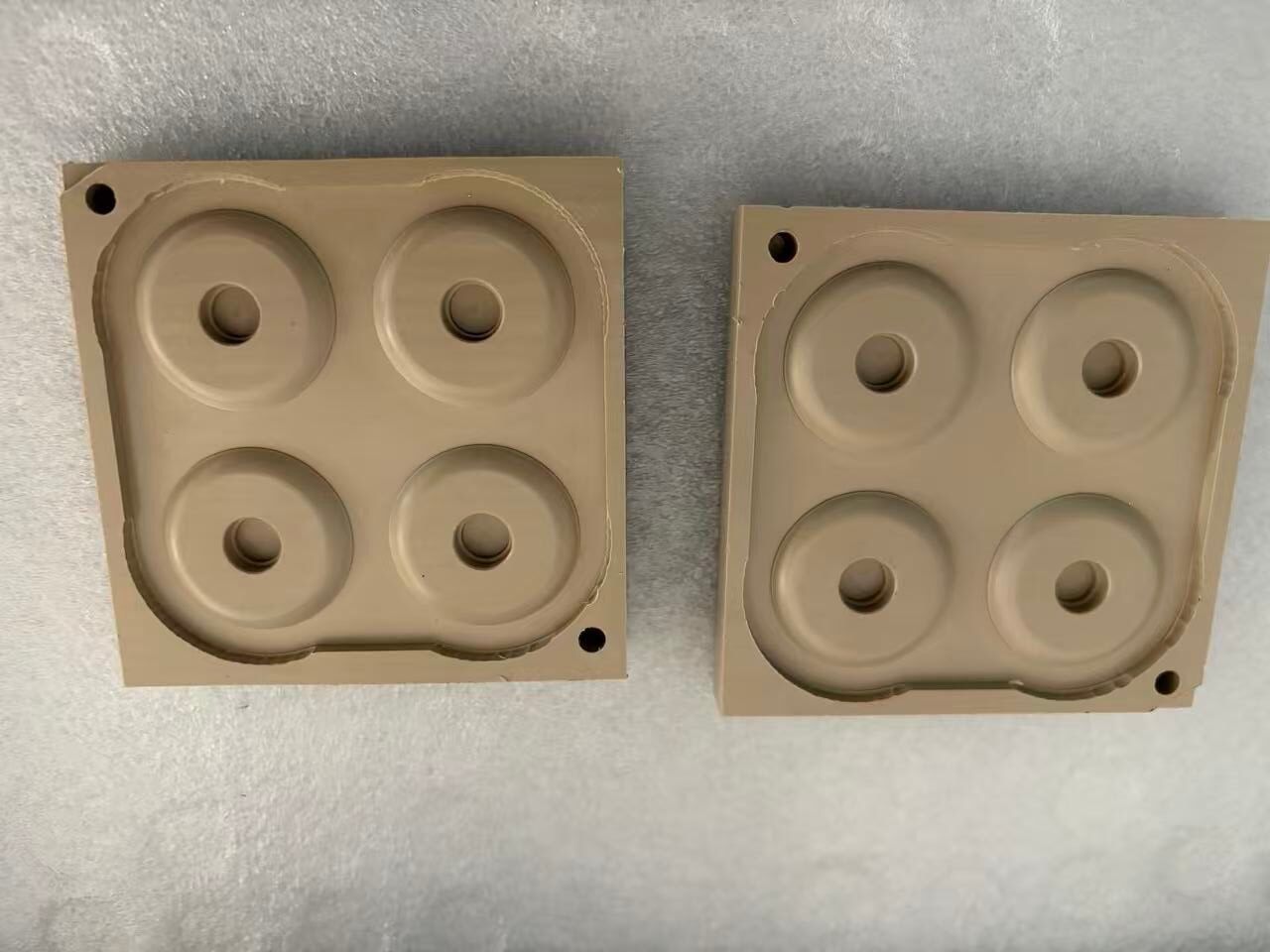
Introduction: Navigating the Challenges of Precision Machining for Hardened Tool Steels
Hardened tool steel represents one of the most demanding materials in precision CNC machining, combining exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability that push conventional machining technologies to their limits. With hardness levels typically ranging from 45–68 HRC, these materials require specialized tooling strategies, precise parameter optimization, and advanced machining techniques to achieve dimensional accuracy and surface integrity.
As industries increasingly demand longer tool life, higher performance components, and reduced maintenance cycles, the ability to effectively machine hardened tool steels has become a critical competitive advantage.
At our CNC machining facility, the Samshion Rapid team, including our skilled engineers and technicians, has pioneered specialized approaches that overcome the traditional limitations associated with these high-strength materials. Through strategic tooling, parameter optimization, and innovative cooling techniques, we’ve transformed what was once considered “unmachinable” into a core competency. This comprehensive guide explores the technical nuances, advanced methodologies, and practical applications of precision machining for hardened tool steels, drawing on the expertise of the Samshion Rapid team.
Understanding Hardened Tool Steel Properties and Machining Challenges
Material Characteristics and Classification
Tool steels encompass a range of alloy steels formulated for high hardness, abrasion resistance, and cutting-edge retention. The hardening process—heating to specific temperatures followed by quenching—transforms their microstructure to achieve these properties.The Samshion Rapid metallurgical engineers routinely perform hardness mapping, microstructural analysis, and residual stress assessment prior to machining to tailor the process plan for each grade of steel.

Table 1: Common Hardened Tool Steel Grades and Machining Characteristics
| Steel Grade | HRC | Alloying Elements | Applications | Machining Challenges |
| D2 | 58–62 | Cr, Mo, V | Blanking dies, forming rolls, molds | Abrasiveness, tool wear |
| A2 | 57–61 | Cr, Mo | Gauges, punches | Moderate machinability |
| O1 | 58–62 | Mn, Cr, W | Cutting tools, knives | Good machinability |
| H13 | 48–52 | Cr, Mo, V | Die casting, extrusion | Thermal fatigue resistance |
| M2 | 62–64 | W, Mo, Cr, V | High-speed tools | Extreme hardness |
| S7 | 56–58 | Cr, Mo, Si | Shock-resistant tools | Ductility, impact resistance |
Primary Machining Challenges
1.Rapid tool wear due to extreme hardness. Our machinists and technicians carefully select cutting tools and monitor wear in real time to maintain consistent part quality.
2.High cutting forces requiring rigid setups. Engineers design customized fixtures to ensure stability and minimize vibration during machining.
3.Thermal management issues due to poor heat conduction. The Samshion Rapid team employs adaptive cooling strategies, including cryogenic and through-tool cooling, to control temperature at the cutting zone.
4.Surface integrity concerns such as residual stresses. Engineers design machining sequences and finishing passes to manage stress distribution.
5.Dimensional accuracy challenges from springback and thermal effects. The technical team utilizes advanced inspection techniques, including CMM and optical scanning, to verify precision.
Advanced Tooling Strategies for Hardened Tool Steels
Cutting Tool Material Selection
Conventional HSS tools are inadequate. Hardened tool steels require advanced materials:
Table 2: Tooling Recommendations
| Tool Material | Hardness (HV) | Thermal Stability | Best Use | Limitations |
| PCBN | 3000–4000 | >1000°C | Finishing (45–68 HRC) | High cost |
| Ceramic | 1800–2200 | >1200°C | High-speed continuous | Thermal shock sensitive |
| CBN | 3000–4500 | >1000°C | Hard turning | Requires careful edge prep |
| Coated Carbide | 1600–2000 | 800–900°C | Roughing <55 HRC | Limited use at high HRC |
| TiAlN Carbide | 2000–2400 | 900–950°C | Interrupted cuts | Progressive wear |
At Samshion Rapid, we evaluate each tool material carefully to match the workpiece hardness and geometry, ensuring maximum accuracy and minimal tool wear. PCBN demonstrates exceptional performance in finishing hardened steels, maintaining accuracy and surface integrity.
Tool Geometry Optimization
Negative Rake Angle: 5°–7° negative rake improves edge strength, reducing the risk of chipping when cutting high-HRC steels. Our engineers use simulation software to verify cutting edge stresses and refine angles for each tool.
Edge Honing: 0.02–0.05 mm edge honing prevents micro-chipping. Samshion Rapid technicians carefully inspect each insert under optical microscopes to ensure uniform honing and minimal edge defects.
Clearance Angle: 5°–7° clearance reduces rubbing and heat generation. This parameter is crucial for high-speed finishing passes, where excessive friction can compromise surface integrity.
Chipbreaker Designs: Custom chipbreakers are designed for each application to enhance chip evacuation. Engineers consider material ductility, hardness, and feed rates to minimize chip entanglement and maintain smooth cutting conditions.
Samshion design these geometries using simulation software, while machinists validate performance in real production scenarios, creating a feedback loop that continually improves cutting efficiency and part quality.
Optimized Machining Parameters for Hardened Steel
Precision Parameter Selection
Cutting speed:
PCBN: 80–250 m/min
Ceramics: 150–350 m/min
Feed rate:
Turning: 0.05–0.15 mm/rev
Milling: 0.05–0.10 mm/tooth
Depth of cut:
Finishing: 0.1–0.5 mm
Roughing: 0.5–2.0 mm
Coolant: Dry or MQL to avoid thermal shock
Studies show surface roughness decreases with increased cutting speed in hard turning—but high speeds may reduce tool life. Samshion Rapid’s team monitors all parameters in real time, leveraging the expertise of our skilled machinists and engineers to maintain part integrity and achieve repeatable results.
Adaptive Machining Strategies
Hardened steels require flexible machining strategies that respond to real-time cutting conditions. Samshion Rapid has developed adaptive processes that incorporate the following:
1.Trochoidal Milling: Reduces heat and cutting forces by limiting the tool’s engagement with the material. Engineers define trochoidal paths to optimize material removal while maintaining spindle stability.
2.High-Speed Machining: Shifts heat into chips instead of the workpiece, preserving microstructure. Technicians monitor spindle power and torque to ensure cutting efficiency without exceeding thermal limits.
3.Progressive Roughing: Reduces residual stress accumulation in high-hardness steels. By removing material in multiple controlled passes, Samshion Rapid ensures minimal distortion and consistent dimensional accuracy.
4.Vibration-Damping Tools: Special tool holders and damped shanks suppress chatter during high-speed cuts. Engineers evaluate tool-holder combinations to maximize stability for long-reach or slender workpieces.
Specialized Techniques for Hardened Steel Components
Thermal Management
Cryogenic machining with LN₂
Through-tool coolant for drilling
Compressed air cooling for dry machining
Cutting parameter tuning to control heat generation
Surface Integrity Enhancement
1.Light finishing passes (0.05–0.10 mm): Technicians execute finishing operations with precision to achieve smooth surfaces without altering part geometry.
2.Residual stress control: Engineers optimize roughing and finishing sequences to manage internal stresses, enhancing component longevity.
3.Microstructure preservation: Machinists and engineers jointly monitor cutting temperatures to avoid tempering or phase changes in the steel.
4.Post-process polishing or superfinishing: Our skilled technicians apply controlled mechanical polishing to achieve superior surface finishes, crucial for tooling, aerospace, and automotive applications.
Quality Assurance for Hardened Steel Components
Surface Integrity Verification
Surface roughness: Ra < 0.8 μm
Residual stress checks via X-ray diffraction
Microhardness testingWhite layer detection
Dimensional Validation
CMM inspection (0.0003 mm accuracy)
Optical scanning for curved surfaces
Functional fixturing
SPC monitoring
Industry Application Case Studies
Based on some previous cases, Samshion Rapid have demonstrated our solutions for processing some high hardness parts.
Case Study 1: Precision Blanking Die Components (D2 Steel)
Challenges:
60–62 HRC, clearance within 0.005mm.
Solution:
Rough → heat treat → PCBN finishing
Trochoidal milling
Custom fixturing
Temperature monitoring
Results:
Surface roughness 0.4 μm
40% longer service life
Samshion Rapid engineers executed the above with precise planning and monitoring, ensuring the die components met stringent tolerance and surface finish requirements.
Case Study 2: High-Performance Injection Mold (H13 Steel)
Challenges:
HRC 48–50, intricate cooling channels.
Solution:
High-speed machining with coated carbide
Precision tool-path optimization
Through-tool coolant drilling
Controlled EDM/texturing
Results:
Excellent surface quality 25% reduced cycle time
Case Study 3: Aerospace Gear Cutting Tools (M2 Steel)
Challenges:
63–64 HRC, precision edge geometry.
Solution:
Soft machining → heat treat → final CBN machining
Customized edge prep
Full CMM inspection
Results:
30% improved tool life
Higher consistency in gear manufacturing
Technical Comparison: Hard Machining vs. Traditional Methods
Hard Machining vs. EDM
Advantages of hard machining:
No recast layer
Faster material removal
More flexible geometry capability
No dielectric fluids
Hard Turning vs. Grinding
Advantages of hard turning (PCBN):
More flexible
Produces compressive stresses
Dry machining
Complex geometry
Future Trends in Hardened Steel Machining Technology
Manufacturing Technology Trends
AI-driven real-time parameter optimization
Hybrid additive + subtractive workflows
Digital twin machining
Sustainable cutting methods
Tooling & Equipment Advancements
Nanostructured coatings
Sensor-embedded smart tools
Adaptive closed-loop controls
High-speed, high-torque spindles
Conclusion
Hardened tool steel machining represents the pinnacle of precision manufacturing, demanding specialized expertise, advanced equipment, and rigorous process controls. The exceptional properties of these materials—outstanding wear resistance, high hardness, and thermal stability—make them indispensable for demanding applications across tooling, aerospace, automotive, and energy industries. However, realizing these advantages requires comprehensive understanding of the material’s machining characteristics and implementation of optimized strategies throughout the manufacturing process. Samshion Rapid team of engineers, technicians, and machinists integrates advanced CNC capabilities with deep material knowledge to deliver reliable high-precision results across tooling, aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors.
With proven success across complex applications and investment in future-ready technologies, we arefully equipped to handle your next hardened steel machining project.
Contact us to discuss your application requirements.