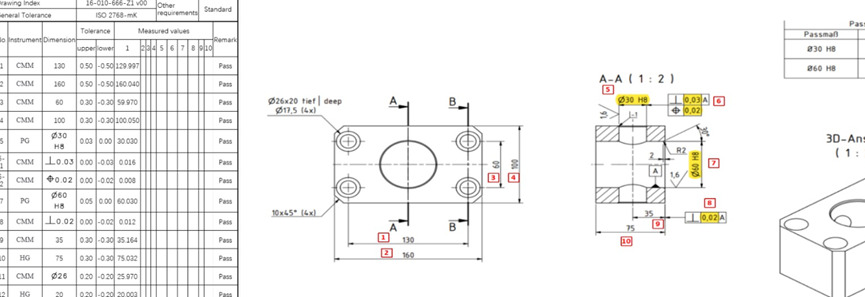
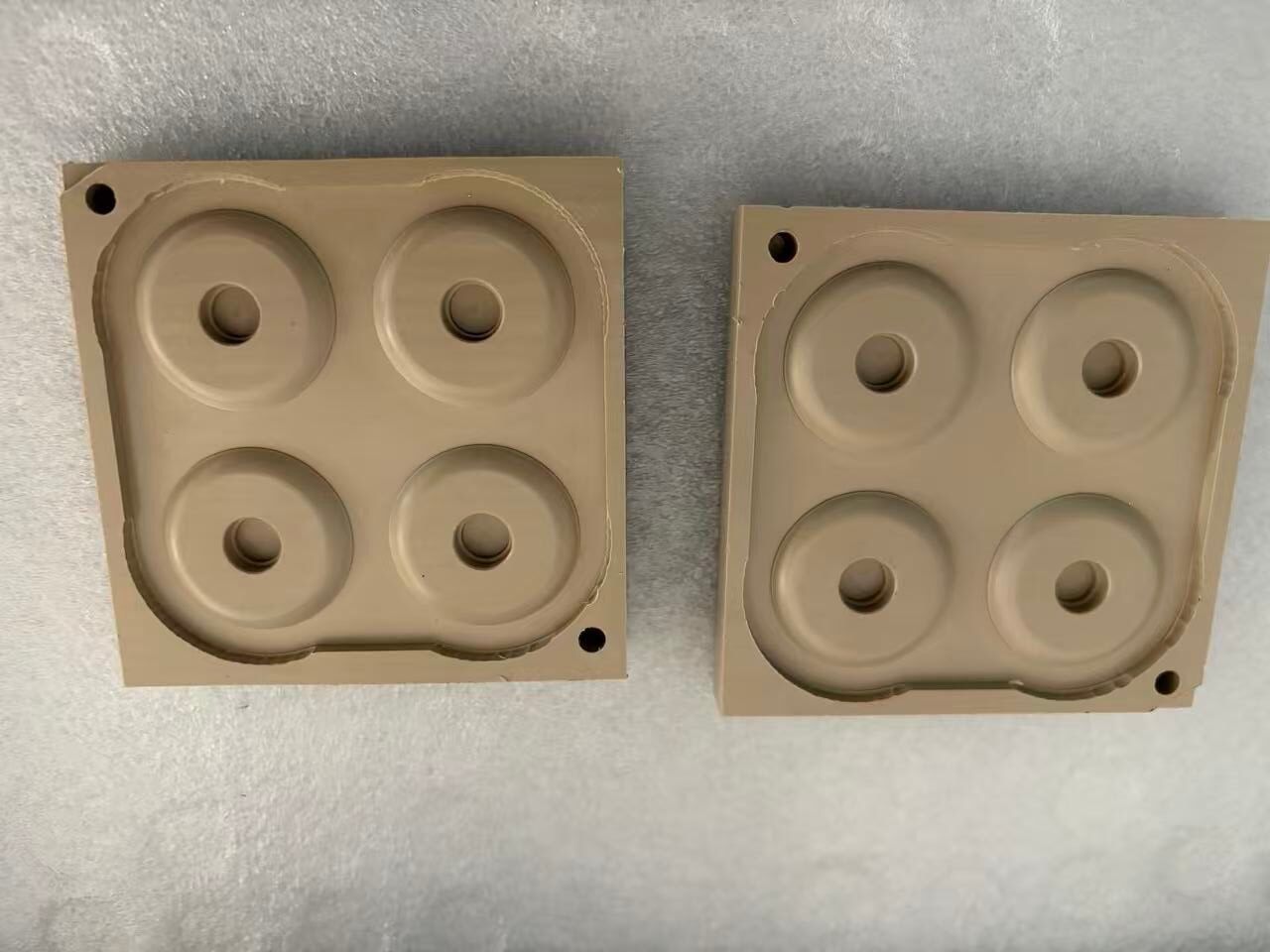
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) is a top-tier engineering thermoplastic commonly employed in CNC machining because of its thermal resistance, chemical durability, dimensional precision and mechanical robustness. In large-scale CNC machining ore prototype production, PPS has gained popularity as a preferred material for reliable components, across aerospace, automotive, electronics, semiconductor machinery and industrial sectors.Samshion Rapid utilizes its expertise in CNC machining of high-performance materials to deliver clients optimized and efficient PPS processing solutions. Additionally this material is seldom. Is often unknown, to many companies. Therefore we have developed this guide offering a detailed overview of PPS material characteristics, benefits of CNC machining suggested processing techniques, machining parameters, design factors and common uses. Hope to assist engineers, designers, and procurement specialists in gaining a better understanding of how to effectively process PPS parts to meet the demands of rapid prototyping, small-to-medium batch production, and even large-scale production via molds.
What Is PPS Material?
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polymer characterized by a molecular structure composed of aromatic rings and sulfur atoms. This unique structure gives PPS exceptional resistance to heat, chemicals, and mechanical fatigue.
Compared with common engineering plastics such as Nylon (PA), Acetal (POM), or Polycarbonate (PC), PPS offers superior performance in extreme environments, making it suitable for demanding CNC machining applications.
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is generally priced in the range of USD $47–$78 per kilogram, depending on material grade, supplier, and purchase volume. Compared with other high-performance plastics, PPS offers a strong balance between cost and performance. For example, PEEK is significantly more expensive, typically costing $100–$180 per kilogram, making it suitable only for the most demanding applications. PTFE usually falls in the $10–$25 per kilogram range, but its lower rigidity and machinability can limit its use in precision CNC machining. In contrast, common engineering plastics such as ABS, Nylon (PA6), Polycarbonate (PC), and HDPE are much more affordable, often priced between $3–$5 per kilogram, though they cannot match PPS in high-temperature resistance, chemical stability, or dimensional accuracy.
Key Material Properties of PPS
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is distinguished by a combination of material properties that make it highly valuable for demanding CNC machining applications. Understanding these characteristics is the first step toward successful part design and manufacturing:
Heat Resistance: PPS preserves its physical characteristics and mechanical strength supporting a constant service temperature range of 200–220°C. This superior thermal capability enables machined components to function dependably in elevated-temperature conditions.
Exceptional Dimensional Consistency: The substance demonstrates minimal moisture uptake and a reduced thermal expansion coefficient resulting in outstanding dimensional consistency. This is essential for Samshion Rapid precise-tolerance tasks, within the semiconductor and electronics sectors guaranteeing that components stay accurate under humid conditions.
Exceptional Chemical Durability: PPS exhibits stability and resistance against various acids, alkalis, fuels and solvents making it perfect, for parts subjected to harsh chemicals.
Elevated Mechanical Durability: The polymer offers stiffness and mechanical durability guaranteeing structural soundness and resistance to deformation especially under high temperature conditions.
Superior Electrical Insulation: PPS possesses electrical insulation characteristics, which is why it is commonly utilized in connectors, insulators and electronic enclosures.
Intrinsic Flame Resistance: It possesses natural flame resistance generally achieving the UL94 V-0 classification without incorporating flame- substances. This is an aspect for Samshion Rapid clients, in the aerospace and consumer electronics industries who need to comply with stringent safety and fire regulations.
These characteristics collectively make PPS ideal for precision CNC machining parts that require long-term stability, tight tolerances, and reliable performance under challenging operational conditions.
Which CNC Machining Processes Are Common for PPS?
PPS is compatible with a wide range of CNC machining operations, making it highly versatile for producing complex part geometries required in demanding industries. Samshion Rapid utilizes the following core processes to fully exploit the material’s properties:

CNC Milling
CNC milling is the most common and flexible method for machining PPS parts. It allows for precise creation of complex contours, deep pockets, intricate slots, and other critical precision features. To achieve optimal results, high-speed milling combined with proactive, aggressive chip evacuation is strongly recommended to prevent localized heat buildup and maintain the integrity of the finished surface.
CNC Turning
PPS supports accurate drilling and tapping operations. Finished threaded holes maintain good mechanical strength, particularly when designers follow recommendations for appropriate thread engagement lengths. When tapping, Samshion Rapid prefers sharp, high-rake tooling and optimized retraction speeds to ensure clean thread profiles and reduce material stress.
Drilling and Tapping
PPS supports accurate drilling and tapping operations. Threaded holes maintain good strength, especially when designed with appropriate thread engagement length.
Secondary Operations
Following the CNC tasks secondary procedures are essential to meet final specifications and confirm prototypes:
Surface Finishing: Fine-tuning the surface texture to meet aesthetic or functional requirements.
Deburring: Removing sharp edges and ensuring dimensional integrity, especially on small features.
Precision Reaming: Achieving highly accurate hole diameters and superior interior surface finishes for tight-fit applications.
Prototype Assembly Verification: Assembly inspections on PPS prototypes are conducted to confirm integration and operational effectiveness prior, to moving into mass production.
What Are the Advantages of PPS in CNC Machining and Prototyping?
PPS offers a strong balance between performance and cost when compared to other high-performance plastics such as PEEK or PTFE. This unique balance makes PPS especially attractive for rapid prototyping and the manufacturing of functional CNC machining prototypes.
Key Advantages in CNC Machining
Excellent Machinability
PPS can be efficiently machined using standard CNC milling, drilling, and turning equipment. It is recognized for its ability to produce clean cuts, minimal burrs, and consistent surface finishes when proper tooling and cutting parameters are used. This excellent machinability helps shorten CNC cycle times and reduces post-machining cleanup, optimizing the overall manufacturing process.
High Dimensional Accuracy
Due to its inherently low thermal expansion and minimal moisture absorption, PPS maintains outstanding dimensional stability both during and after the CNC machining process. This critical material property makes it an ideal choice for producing tight-tolerance components where precision and repeatability are essential, especially in demanding CNC applications.
Thermal and Chemical Stability
CNC-machined PPS parts can operate reliably in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments, which is critical for aerospace, automotive, and semiconductor equipment.
Ideal for Prototyping and Low-Volume Production
PPS CNC machining, as performed by specialists such as Samshion Rapid, enables fast design validation and functional testing of parts. This approach supports bridge production and low-to-medium volume manufacturing without the high initial investment and long lead times associated with injection molding tooling. For engineers who require fast and reliable PPS prototypes, CNC machining remains the most practical and efficient solution.
What CNC Machining Parameters Are Recommended for PPS?
Achieving optimal surface quality and dimensional accuracy in PPS components depends heavily on selecting the correct CNC machining parameters. The primary objective is to maximize material removal while effectively controlling heat generation, which is critical when machining thermoplastics.
Tooling Recommendations
To successfully machine PPS, sharp carbide tools are highly recommended due to their excellent edge retention and durability. Samshion Rapid’s engineers emphasize that tools with highly polished cutting edges are essential, as they minimize frictional heat—a common challenge when machining PPS. Operators should avoid using dull tools, as these significantly increase friction, leading to excessive heat buildup and potential material melting or smearing.
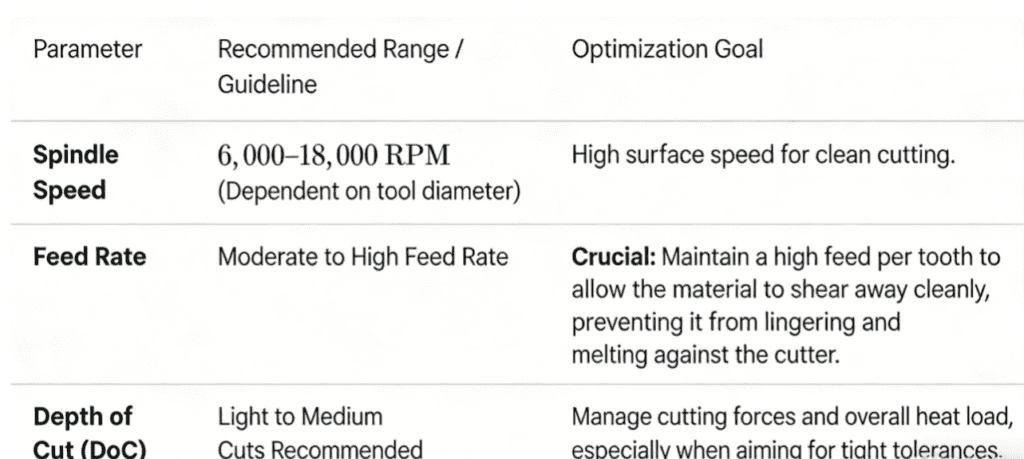
Cutting Parameters (Typical Range)
Please refer to the diagram below, where we have provided optimal data ranges for parameters such as feed rate and spindle speed. This information is intended for engineers involved in CNC machining of PPS materials for analysis purposes.
Cooling and Chip Control
Effective thermal management and chip evacuation are essential when machining PPS. At Samshion Rapid, we find that an air blast is typically sufficient and preferred, as it removes chips quickly while minimizing temperature fluctuations. Excessive use of liquid coolant should be avoided to prevent thermal shock, which can cause microscopic cracks or dimensional instability. Most importantly, continuous chip evacuation is critical to prevent hot chips from re-melting or fusing back onto the workpiece surface, a primary cause of poor surface finish and dimensional inaccuracies in PPS CNC machining.
How Should PPS Parts Be Designed for CNC Machining?
Creating components tailored for CNC machining can greatly enhance production feasibility minimize tensions and decrease expenses. Samshion Rapid adheres to these practices when guiding clients, on PPS part design:
Best Design Practices
Consistency in Wall Thickness: Ensure the wall thickness remains consistent across the part geometry. This is essential for thermoplastics such, as PPS to reduce stresses and avoid warping or deformation during CNC machining and the following cooling phase.
Corner Geometry: Steer of sharp internal angles (under 90°) and implement fillets whenever feasible. Fillets enhance the durability of the component. Minimize stress concentration areas, which is especially crucial for rigid materials such, as PPS.
Tolerance Assignment: Provide tolerance considering the size and purpose of the part. Tight tolerances lead to longer machining durations and higher expenses.
Thread Design: Design threads with adequate engagement length to fully utilize PPS’s mechanical strength, ensuring reliable assembly performance.
Tolerance Considerations
PPS is capable of maintaining tight tolerances, typically achieving ±0.02–0.05 mm, depending on part geometry and the CNC machining strategy employed. For precision assemblies, tolerance requirements should be clearly defined during the prototype stage to allow optimized fixturing and tool paths for critical features.
What Are the Typical Applications of CNC Machined PPS Parts?
Thanks to its blend of thermal, chemical and mechanical properties PPS is extensively employed in numerous industries for challenging end-use CNC-machined parts.
In aerospace it finds application in connectors, structural brackets, high-temperature insulating parts and precision bushings. Within the field PPS parts include sensor housings—particularly, for exhaust sensors—fuel system elements and transmission and pump components that must withstand harsh fluids and elevated temperatures.
In electronics and semiconductor tools ,PPS is utilized in fixtures insulating parts, wafer handling devices and burn-in sockets requiring high purity and thermal durability. In chemical machinery, PPS serves for valve elements, pump casings, chemical agitators and corrosion-resistant structural components subjected to constant chemical exposure.
How Does PPS Compare to Other High-Performance Plastics?
When choosing a material for a CNC task PPS presents benefits over other advanced polymers. In relation to PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone), PPS is more cost-effective while still delivering outstanding thermal and chemical resistance for uses functioning under PEEK’s maximum temperature limits. In comparison with PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), PPS provides stiffness improved mechanical toughness, enhanced dimensional stability and superior ease of machining. These advantages make PPS an ideal choice for both functional prototypes and cost-effective, high-volume end-use CNC-machined parts produced by specialists like Samshion Rapid.
How Does PPS Compare to Other High-Performance Plastics?
PPS CNC machining plays an twofold function in the contemporary product development process: facilitating swift innovation and offering flexible manufacturing capabilities.
Rapid Prototyping: Minimizing Development Risk
During CNC prototype machining of PPS enables producers to rapidly validate designs evaluate performance and efficiently refine intricate parts. Since PPS CNC prototypes frequently mimic the thermal, chemical and mechanical characteristics of the ultimate injection-molded material this method greatly lowers development risks and speeds up the time-, to-market process. Samshion Rapid focuses on providing PPS prototypes that offer precise performance insights removing the unpredictability commonly linked to standard prototyping materials.
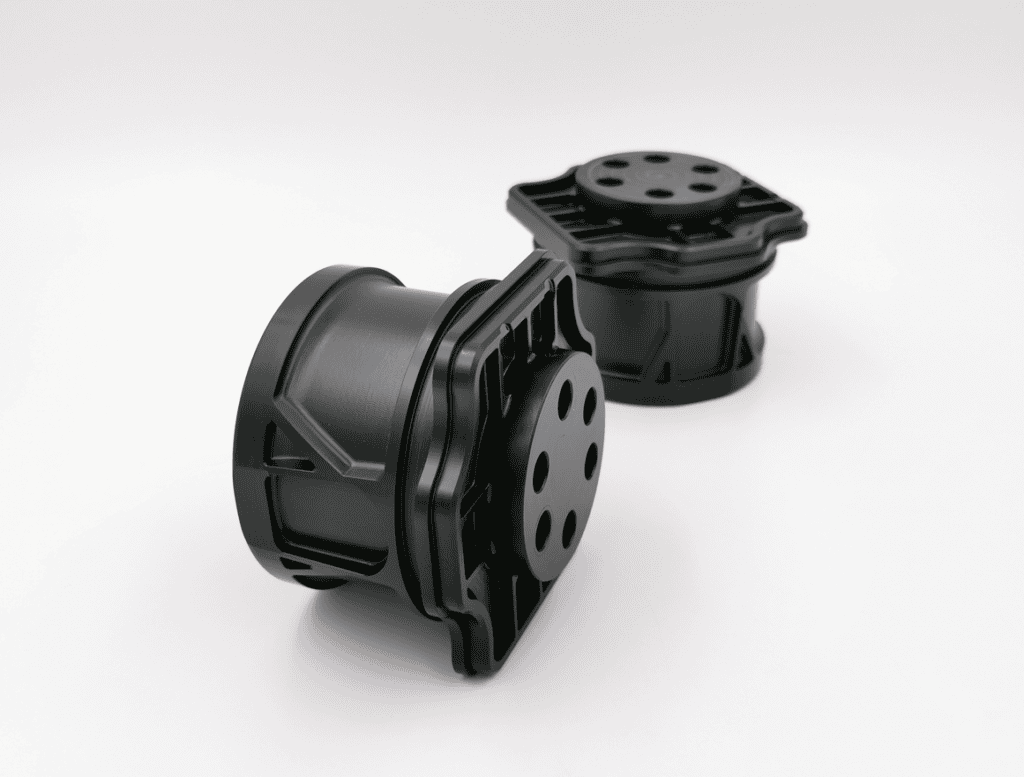
Low-to-Medium Volume Production: Adaptability and Cost-Effectiveness
For low-to-medium volume manufacturing, PPS CNC machining offers exceptional adaptability, high accuracy, and cost-effectiveness without the need for expensive and time-consuming injection molds. This is particularly valuable for specialized industrial, aerospace, or medical components where annual volumes do not justify tooling costs. CNC production enables rapid design updates and customization across batches. By leveraging efficient CNC centers, we can provides a highly accurate and scalable manufacturing bridge, ensuring consistency from the first prototype to the final production run.
How Is Thermal Stress Managed During PPS CNC Machining?
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) similar to semi-crystalline thermoplastics may accumulate internal stresses throughout production (extrusion or molding) and notably, during high-speed CNC machining because of frictional heat and swift material extraction. Without management these stresses may cause deformation, cracking or dimensional changes especially in thin-walled or intricate shapes.
Stress Relief Procedures for PPS Stability
To guarantee the dimensional standards that customers demand us frequently applies a regulated stress relief (annealing) technique:
Initial Machining: The PPS stock is roughly machined near its measurements.
Thermal Cycling: The machined component undergoes a regulated heat treatment within an oven. The temperature is generally maintained slightly under the materials glass transition temperature (Tg) 90°C, for typical PPS for a duration of several hours. This process permits the polymer chains to ease and eliminate stresses without melting the substance.
Controlled Cooling: The component is gradually cooled to temperature to avoid the sudden creation of new stresses.
Final Machining: The component is sent back, to the CNC machine for the concluding, finishing cuts.
Why Stress Relief Matters?
Reduces Warping: The best way to avoid parts warping -machining is, through stress relief, which guarantees that final tolerances stay consistent across time and temperature variations.
Improves Consistency: In production batches this method guarantees uniformity and repeatability of intricate components, which is crucial to Samshion Rapid dedication, to quality.
Best for Precise Tolerances: This stage is essential when precise tolerances (±0.02 mm) or thin walls are needed since these shapes are especially vulnerable, to internal stress impacts.
By implementing strict stress relief protocols, Samshion Rapid ensures that the dimensional stability of PPS parts is optimized for the most demanding high-temperature and structural applications.
Your PPS Machining Partner——Samshion Rapid
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is a top-tier engineering plastic that connects material properties with economical manufacturing processes. Its remarkable thermal stability, excellent chemical resistance and high dimensional precision render it ideal, for CNC machining, quick prototyping and the fabrication of challenging end-use parts.
For sectors demanding performance in extreme environments—ranging from engine bays to aggressive chemical setups—PPS provides the essential toughness and resilience without the expensive price tag linked to materials, like PEEK.
By grasping the characteristics of PPS using suitable CNC machining settings and adhering to effective design guidelines manufacturers can maximize the material’s distinct benefits to create dependable premium components, for various sectors.
Samshion Rapid serves as a dedicated partner in realizing the full potential of PPS. We combine specialized high-speed CNC machining capabilities with deep material expertise to ensure that PPS prototypes and low-volume production parts meet the tightest tolerances and highest performance requirements.