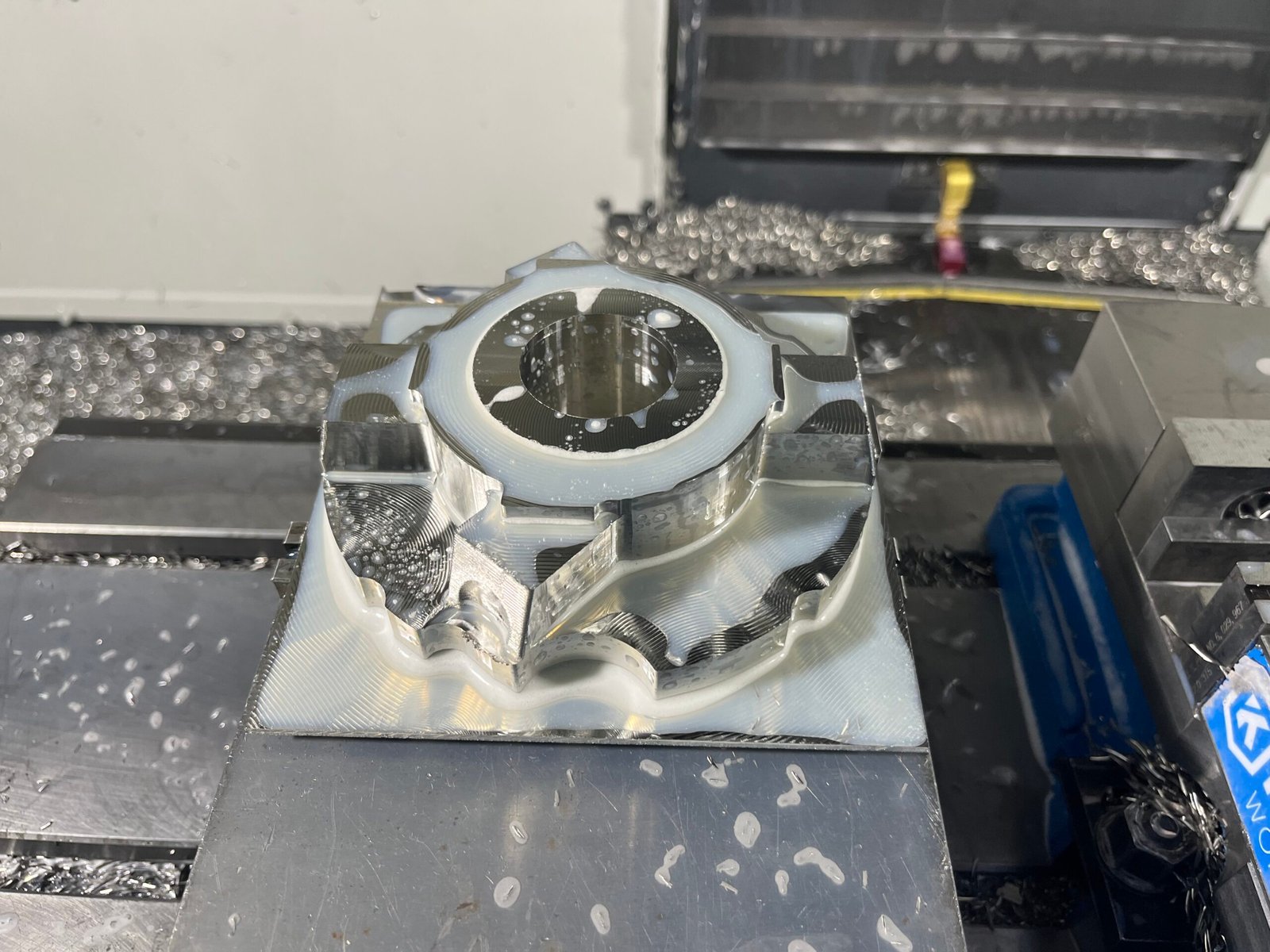
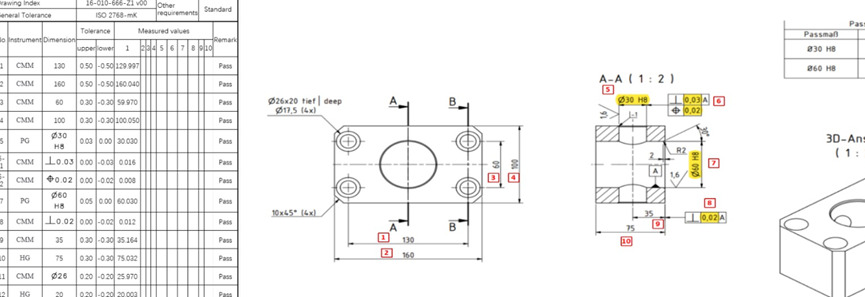
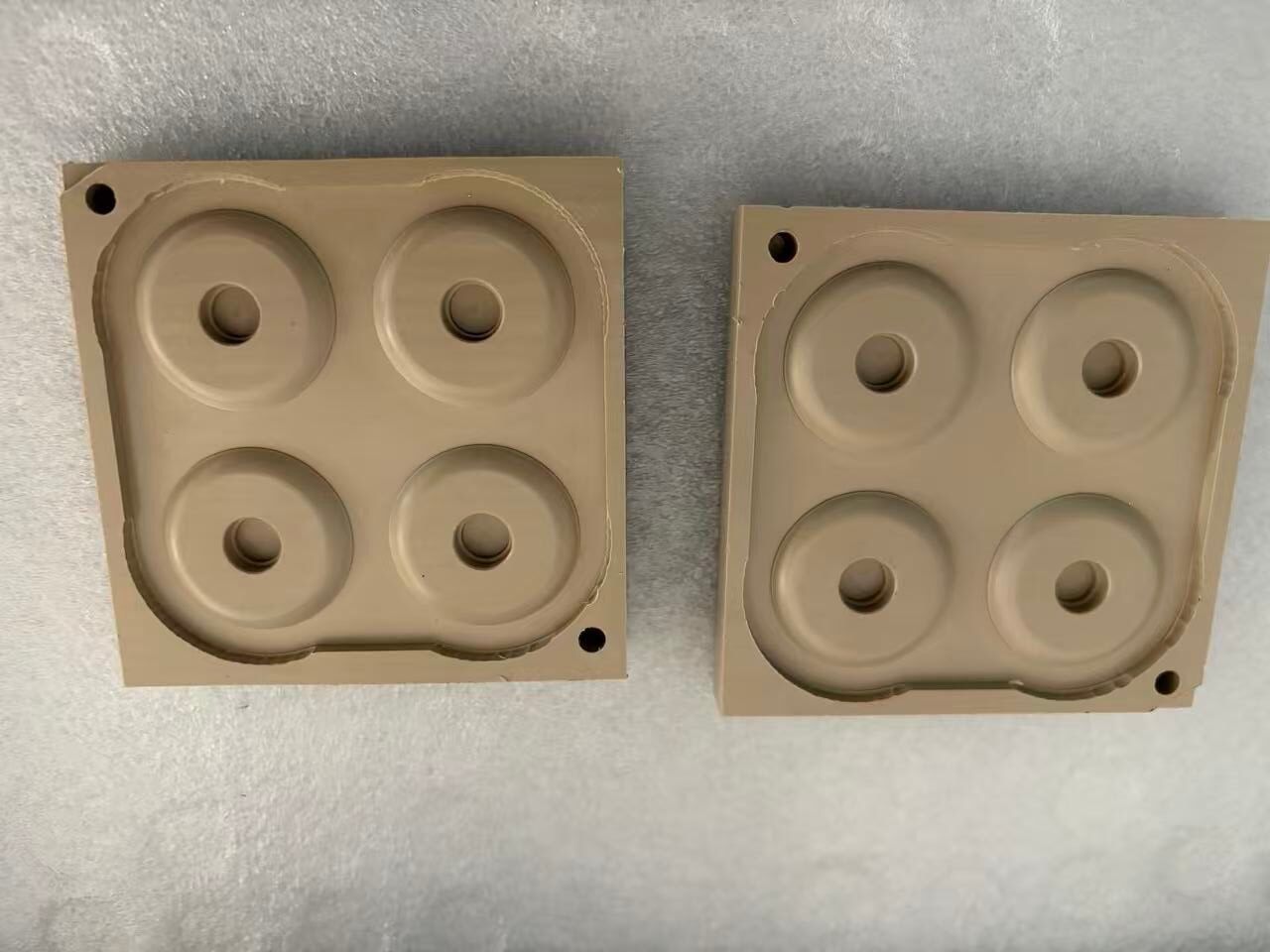
Samshion Rapid’s production team takes pride in using end milling not just as another machining step—but as a core capability tailored to handle complex geometries and demanding surface finishes using our Haas CNC centers.
When machining materials like stainless steel, aerospace alloys, or engineering-grade plastics, we precisely control every cut—only removing material where needed. This allows us to consistently achieve dimensional accuracy within ±0.002 mm and surface finish levels down to Ra 0.8 µm, standards required by high‑end sectors such as automotive, medical devices, and electronics components.
What makes our process unique is our workflow integration: single-fixture runs with adaptive parameter adjustments between roughing and finishing. This seamless transition—courtesy of Haas intelligent machine control and optimized toolpaths—reduces setup changes and slashes lead time by around 40% compared to traditional segmented processes.
At Samshion, end milling isn’t just a technique—it’s a scalable solution that enables both prototyping flexibility and production efficiency, delivering parts that meet the highest accuracy and throughput demands.
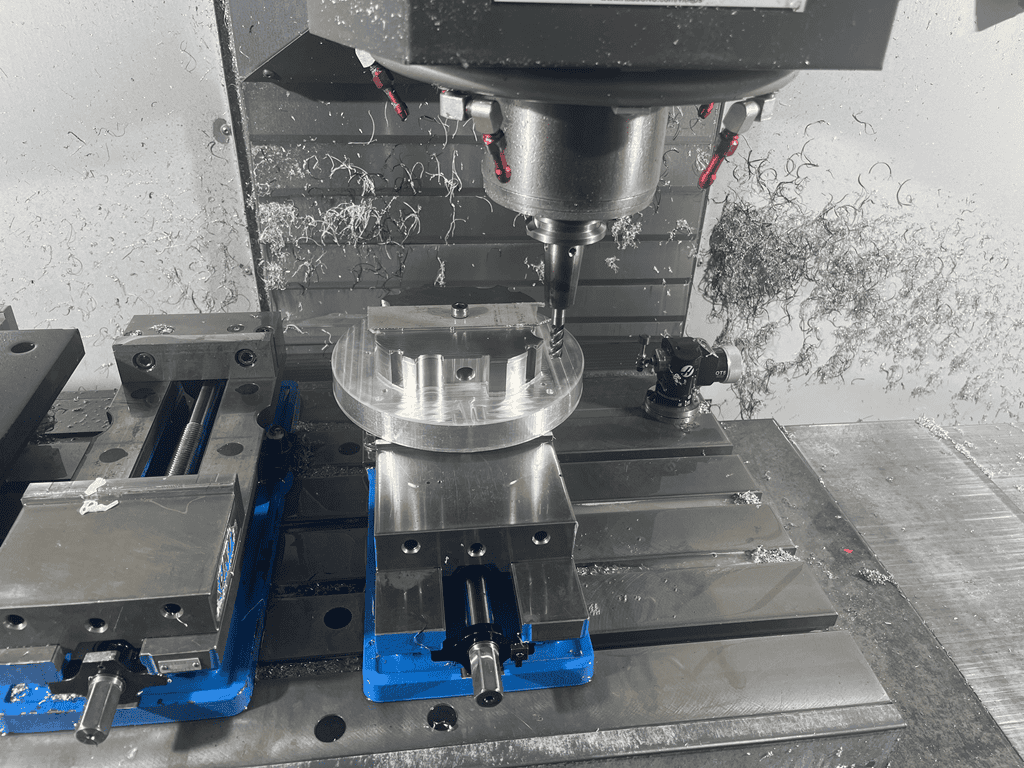
What Is End Milling?
Our Haas CNC machining centers perform precision end milling operations using specialized cutting tools that remove material both vertically and horizontally. Unlike single-direction tools like drills or face mills, our end mills feature unique helical flute designs that enable multi-axis machining capabilities – a critical advantage when producing complex mold components, aerospace parts, and medical device prototypes.
Samshion Rapid’s engineering team selects end mills based on:
1.Cutting diameter (from micro-tools to 32mm+ for heavy roughing)
2.Flute configuration (2-6 flutes for optimal material removal)
3.Specialized coatings (TiAlN/TiCN for extended tool life)
The Haas Ultra High-Speed Spindle (15K-20K RPM) combined with our optimized toolpaths achieves surface finishes ranging from Ra 6.3μm for roughing to sub-Ra 0.8μm for finishing operations.
Key process advantages:
- Advanced Tool Geometry – Variable helix angles and chip breakers reduce harmonic vibration during deep cavity machining
- Efficient Material Removal – Indexable end mills with carbide inserts handle heavy roughing (19-50mm diameters) at 30% lower cost than solid carbide tools
- Precision Finishing – Ball nose and corner radius end mills produce complex 3D contours with ±0.01mm tolerance.
Why End Milling Is Essential?
End milling is a critical process at Samshion Rapid, enabling us to machine everything from simple slots to complex 3D contours with precision and efficiency on our Haas CNC milling centers. This versatility comes from advanced tool designs, precise CNC control, and optimized machining strategies.
Our Haas CNC machines deliver high accuracy (±0.05 mm) while maintaining fast material removal rates, often eliminating the need for secondary operations and saving time and costs. Whether working with aluminum, titanium, steel, or plastics, we use specialized carbide end mills—such as variable-helix roughers or DLC-coated finishers—to ensure optimal performance, smooth chip evacuation, and long tool life.
To maximize productivity, we employ CAM-optimized toolpaths like adaptive clearing and trochoidal milling, reducing cycle times by up to 40% compared to traditional methods. Multi-flute designs allow deeper cuts without overloading the tool, further enhancing efficiency.
A key advantage is single-setup machining—our Haas mills handle roughing, semi-finishing, and finishing in one clamping, minimizing errors and improving consistency. With rotary tool changers and real-time monitoring, we can run machines unattended, boosting throughput.
Additionally, advanced coatings like AlTiN and DLC extend tool life up to four times, especially in high-temperature alloys, lowering costs per part. This ensures we maintain tight tolerances and profitability, even with challenging materials.
At Samshion Rapid, end milling is a cornerstone of our precision machining capabilities, allowing us to produce high-quality parts efficiently. By leveraging Haas CNC technology, smart tooling, and optimized processes, we deliver reliable results across industries.
The Evolution of End Milling Technology
End milling has undergone significant advancements since its inception, evolving from basic metal-cutting methods to today’s high-precision CNC machining processes. The concept of milling first emerged in the early 19th century, primarily for creating flat surfaces using rotating cutters. However, true end milling—where cutting occurs at the tool’s tip and periphery—did not become widespread until the late 1800s, thanks to advancements in high-speed steel tooling and growing industrial demand for intricate part geometries.
A major breakthrough came in 1918 with Carl A. Bergstrom’s patented helical-flute end mill, which replaced earlier straight-flute designs. This innovation allowed for smoother cutting action, reduced vibration, and improved chip evacuation, making it especially valuable for machining tough metals. The helical-flute design soon became an industry standard, enabling greater precision and repeatability in manufacturing.
The introduction of CNC technology in the 1970s revolutionized end milling by automating tool movements, enabling precise feed and speed control, and allowing complex multi-axis machining. This shift from manual operation to computer-controlled processes dramatically improved efficiency and accuracy.
Further progress came in the 1980s with the adoption of solid-carbide end mills, which offered superior rigidity and heat resistance compared to traditional high-speed steel tools. These advancements supported higher spindle speeds and finer tool geometries, making them ideal for mold making, die manufacturing, and electronics production.
Tool coatings also played a crucial role in advancing end milling capabilities. In the 1990s, titanium-based coatings (TiN, TiAlN) became standard, significantly extending tool life and enabling dry machining of hardened steels. Today, advanced coatings like diamond-like carbon (DLC) and polycrystalline diamond (PCD) are widely used in aerospace and high-performance applications, where extreme wear resistance and thermal stability are essential.
Modern end milling continues to evolve with innovations in micro-grain carbide substrates, adaptive toolpaths, and smart machining systems. These developments allow manufacturers to achieve tighter tolerances, faster cycle times, and longer tool life—solidifying end milling as a cornerstone of precision manufacturing.
How Does the End Milling Process Work?
Samshion Rapid’s machine setup process forms the critical foundation for successful end milling operations. We’ve developed a rigorous protocol for our CNC machines that ensures repeatable precision across all production runs.
Tooling Preparation
We begin by selecting the optimal end mill for each application, considering:
1.Material-specific flute geometry
2.Coating requirements (AlTiN for hardened steels, DLC for aluminum)
3.Cutting diameter and length requirements
Each tool undergoes careful inspection before being mounted in our precision-balanced holders. We use thermal shrink-fit or hydraulic chucks for maximum gripping force and minimal runout, typically maintaining TIR below 0.005mm.
Workholding Solutions
Our technicians employ a variety of workholding methods tailored to part geometry:
1.Kurt-style vises with hardened jaws for standard rectangular workpieces
2.Custom-machined soft jaws for complex contours
3.Modular clamping systems for large or irregular shapes
4.Vacuum plates for thin-walled components
Every setup includes verification of perpendicularity and parallelism to ensure machining accuracy from the first cut.
Machine Calibration
Prior to production, we perform:
1.Spindle warm-up cycles to stabilize temperatures
2.Tool length measurements using laser or touch probes
3.Work coordinate system establishment with probe verification
4.Collision avoidance system checks
Cutting Parameter Optimization
Our process engineers input material-specific parameters:
1.RPM calculations based on tool diameter and SFM requirements
2.Feed rate optimization using chip load calculations
3.Coolant delivery selection (through-tool for deep cavities)
4.Adaptive clearing parameters for roughing operations
This meticulous setup process, combined with our Haas CNC capabilities, allows Samshion to achieve first-part-correct production with exceptional consistency. Our setup documentation system ensures identical conditions for repeat orders, maintaining quality across production batches.
What are the Types of End Mills?
End mills come in various types each designed for specific machining applications with different geometries and features that affect cutting performance and surface finish
The most common classification includes square end mills for general milling operations ball nose cutters for 3D contouring corner radius end mills for durability and roughing end mills with serrated edges for aggressive material removal
Flute count plays a crucial role in performance where two to three flute designs work best for aluminum and non-ferrous materials while four or more flutes are better suited for steel and hard metals with variable helix patterns reducing vibration in challenging materials
Material composition ranges from solid carbide for precision and wear resistance to micrograin carbide for tough cuts cobalt HSS for cost-effective solutions and diamond-tipped options for abrasive composites
Specialized coatings enhance tool life including TiAlN for high-temperature alloys DLC for aluminum machining ZrN for non-ferrous applications and uncoated tools for certain plastics and composites
Unique applications call for specific designs like tapered mills for mold work long-reach tools for deep cavities micro-end mills for small features and thread mills for creating threaded parts
At Samshion Rapid, we carefully select the appropriate end mill type based on material properties feature complexity and required surface finish ensuring optimal performance on our CNC machines for every machining project.
End Mill Geometry and Its Impact on Machining Performance
The physical shape of an end mill fundamentally determines its cutting behavior and application range. Different geometries produce varying chip formation patterns, surface finishes, and tool life characteristics, making proper selection critical for machining success.
Flat-end mills create precise 90° corners and are ideal for general milling operations, while ball-nose cutters excel at complex 3D contouring work. Corner-radius designs combine durability with precision, featuring slightly rounded edges that distribute cutting forces more evenly. For heavy material removal, roughing end mills with their distinctive serrated edges efficiently break up chips during aggressive cutting.
Each geometry serves distinct purposes in the machining process. Some excel at plunging operations, while others are optimized for finishing passes. The tool’s shape also affects its structural rigidity – a crucial factor when working with hard materials or requiring deep cutting depths.
Square End Mills: The Workhorse of Precision Machining at Samshion
At Samshion Rapid, our Haas CNC machines frequently utilize square end mills as fundamental tools for achieving precise 90-degree corners and flat surfaces. These versatile cutting tools feature a flat bottom geometry that makes them indispensable for various milling applications across multiple materials.
Our square end mills are perfect for creating flat surfaces, pockets, and shoulders with accuracy. Thanks to a range of flute configurations, they can be tailored for either aggressive roughing or high-quality finishing, depending on your machining strategy.
To enhance durability and performance, we offer tools with advanced coatings such as TiN (Titanium Nitride) and AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride)—ideal for high-speed applications and machining harder materials like stainless steel or tool steel.
Whether you’re working with metal, plastics, or composites, Samshion delivers reliable cutting tools that help you maintain tight tolerances and improve productivity.
Ball End Mills: Precision Tools for Complex Geometries at Samshion
At Samshion Rapid, we rely on ball end mills to machine intricate 3D contours, curved surfaces, and complex profiles with exceptional precision. These specialized tools feature a hemispherical cutting tip that enables smooth, continuous toolpaths—making them indispensable for mold making, aerospace components, and medical device manufacturing.
The spherical geometry of the tool enables continuous contact with the workpiece, even at shallow engagement depths—reducing vibration, limiting tool deflection, and delivering exceptional surface finishes.
Perfect for mold cavities, die work, medical components, and aerospace parts, ball end mills are indispensable when sharp internal corners are either unnecessary or must be avoided to reduce stress concentrations.
With multiple flute options and optimized helix angles, our cutters ensure efficient chip removal while maintaining tight tolerances across a range of materials and speeds. Whether you’re working with aluminum alloys or hardened steels, Samshion Rapid provides the tools that help bring complex geometries to life.