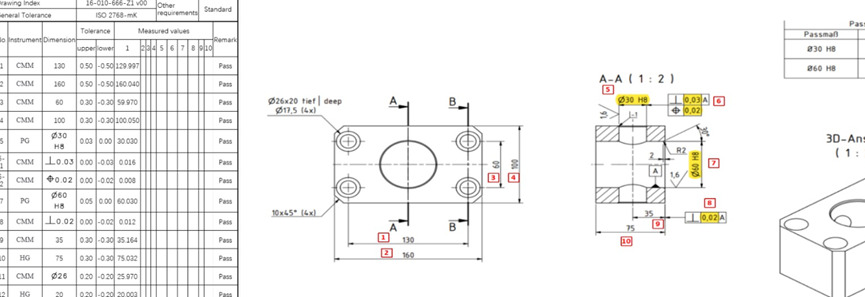
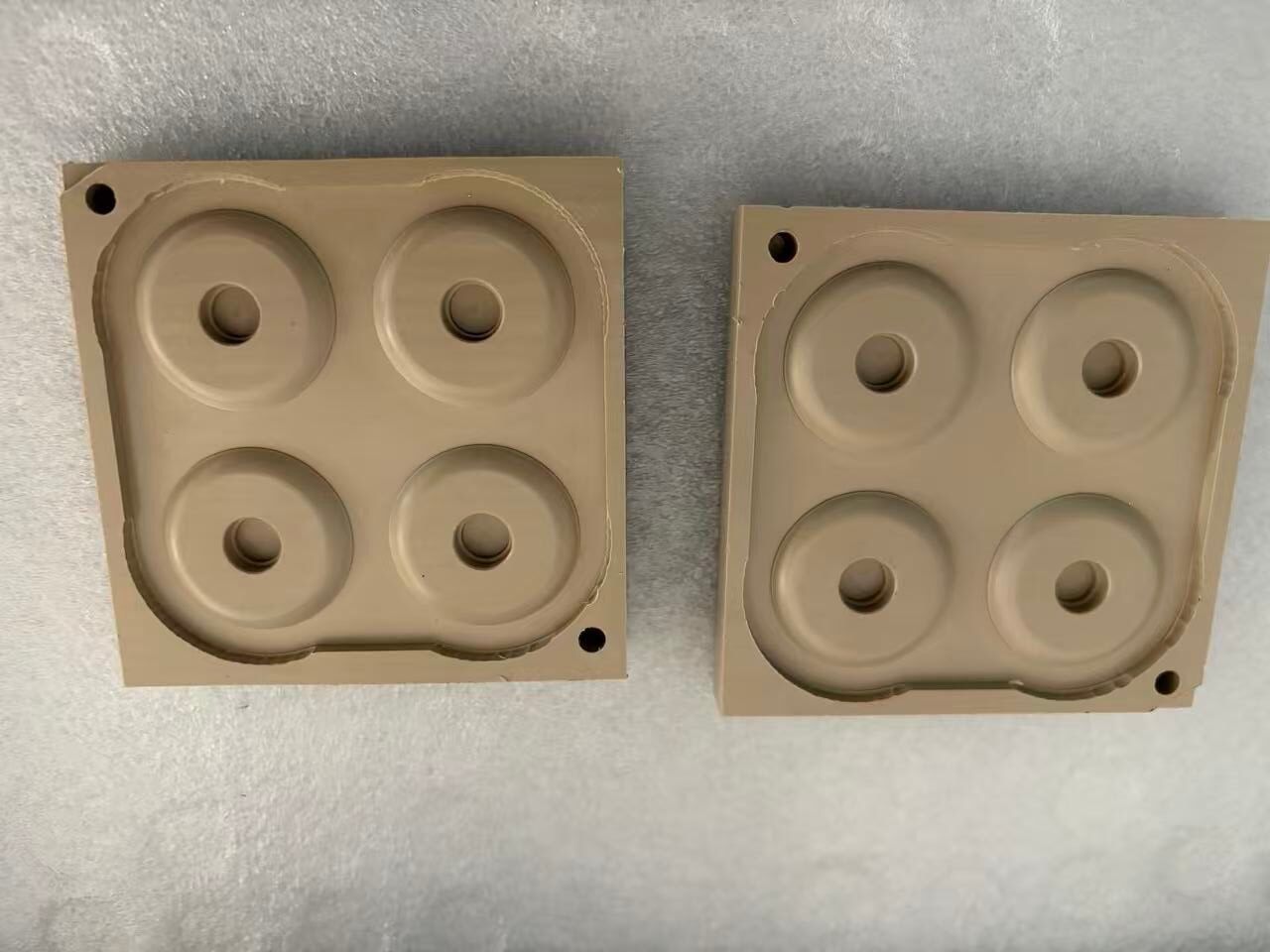
CNC Machining Basics: A Friendly Guide for Beginners
Hey there!
So, you’ve heard about CNC machining and are curious to learn more? You’re in the right place! Let’s sit down and chat about the basics of CNC machining in a way that’s easy to understand.
What Is CNC Machining?
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. In simple terms, it’s a manufacturing process where computers control machine tools to create precise parts from materials like metal, plastic, or wood. Imagine telling a machine exactly how to cut or shape a piece, and it does so with incredible accuracy.
How Does CNC Machining Work? (Let’s Keep It Simple)
Alright, let’s break this down — no engineering degree needed.
Imagine you want to make a custom phone case out of metal or a plastic part for your product. You don’t just grab a tool and start cutting, right? Here’s how CNC machining actually gets the job done — step by step, plain and simple:
1. You Start With a Digital Design (The Blueprint)
Everything begins with a 3D model — basically a digital sketch of the part you want to make. This is usually created using CAD software (that’s short for Computer-Aided Design). Think of it as drawing your idea in 3D so the machine knows exactly what to make.
2. We Turn That Design Into Machine Language (The Instructions)
That design then gets converted into a set of instructions that the CNC machine understands. This code — called G-code — tells the machine how to move, where to cut, how fast to go, and even what tool to use. It’s like programming a robot to follow your recipe exactly.
3. The Machine Gets Set Up (Prepping the Tools)
Before anything starts, the right cutting tools are installed into the machine, the right material is loaded (metal, plastic, etc.), and everything is calibrated. This step ensures accuracy and safety.
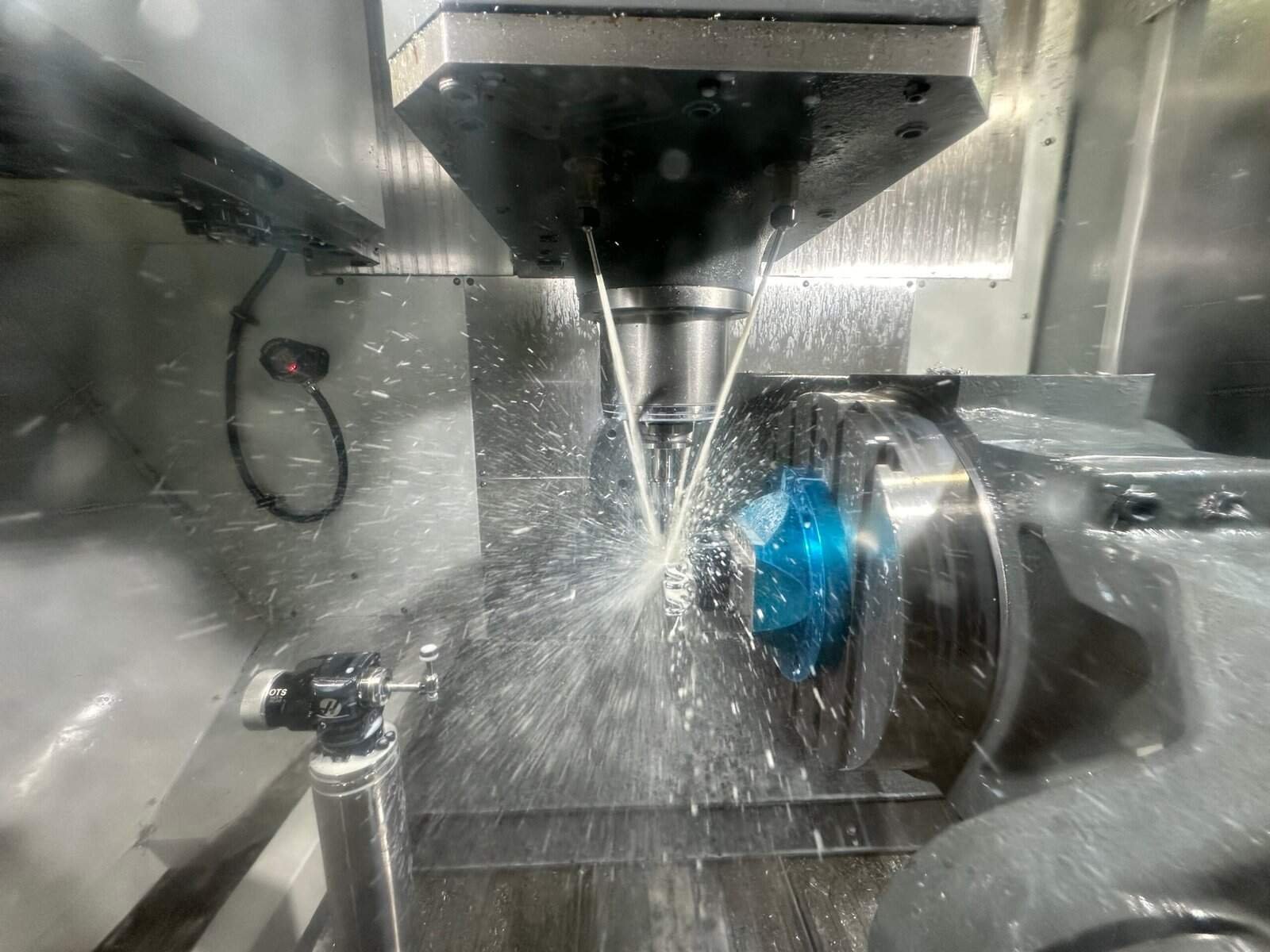
4. It’s Go Time! (The Machining Begins)
Now the CNC machine gets to work. Guided by the G-code, it starts carving, drilling, or milling the material into the exact shape you designed. Depending on how complex your part is, this could take just a few minutes — or a bit longer.
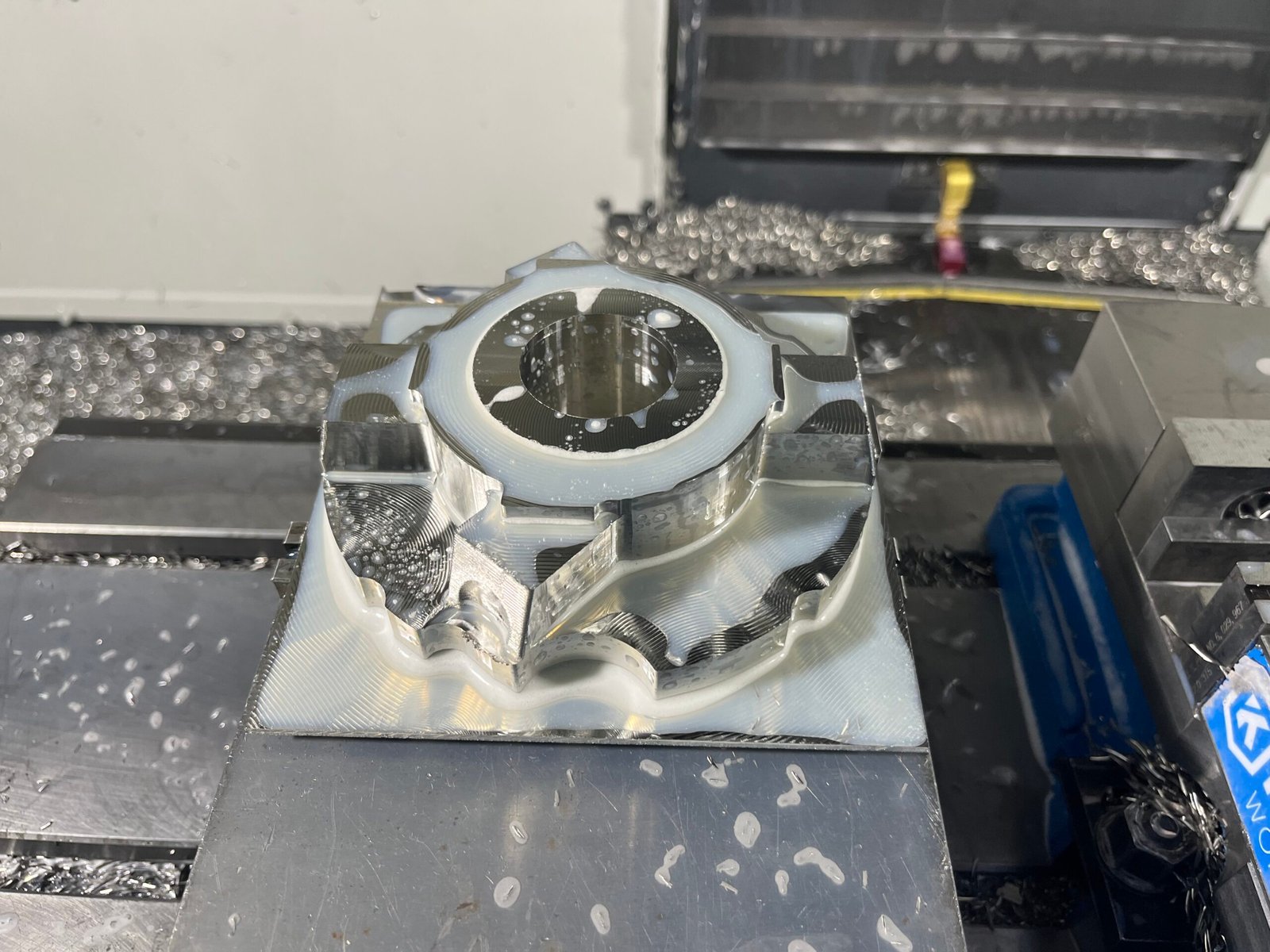
5. We Check the Part (Quality Time)
Once the machining is done, the part is removed, cleaned, and carefully inspected. If needed, we’ll do a quick tweak or polish to make sure it meets all your specs — down to the tiniest detail.
6. Optional: Surface Finishing (The Final Touch)
Depending on what you need, the part might go through surface finishing — like polishing, anodizing, painting, or coating — to make it look great and perform even better.
Types of CNC Machines
There are several types of CNC machines, each suited for different tasks:
CNC Mills: These machines use rotating cutting tools to remove material. They’re great for creating complex shapes.
CNC Lathes: These rotate the material against cutting tools, ideal for producing cylindrical parts.
CNC Routers: Similar to mills but typically used for softer materials like wood or plastic.
CNC Plasma Cutters: Use a plasma torch to cut through metal.
CNC Laser Cutters: Use a laser beam to cut or engrave materials.
Each machine has its unique capabilities, and the choice depends on the material and the desired outcome.
Materials Used in CNC Machining
CNC machines can work with a variety of materials, including:
Metals: Aluminum, steel, brass, copper, and titanium.
Plastics: ABS, polycarbonate, nylon, and PEEK.
Composites: Carbon fiber and fiberglass.
Wood: Hardwoods, softwoods, and plywood.
The choice of material depends on the part’s intended use, required strength, weight, and other factors.
Advantages of CNC Machining
Why choose CNC machining? Here are some compelling reasons:
Precision: CNC machines can achieve incredibly tight tolerances, ensuring each part is made to exact specifications.
Consistency: Once programmed, CNC machines can produce large quantities of identical parts without variation.
Efficiency: Automated processes reduce production time and labor costs.
Flexibility: Easy to switch between different designs or make modifications without the need for new tooling.
Scalability: Suitable for both small prototype runs and large-scale production.
Common Applications
CNC machining is used across various industries:
Aerospace: Creating complex components that require high precision.
Automotive: Manufacturing engine parts, gearboxes, and custom components.
Medical: Producing surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics.
Electronics: Fabricating enclosures, connectors, and heat sinks.
Consumer Products: Developing prototypes and final products like gadgets and appliances.
Getting Started with CNC Machining
If you’re considering CNC machining for your project, here’s a simple roadmap:
- Design Your Part: Use CAD software to create a 3D model of your part.
- Choose the Right Material: Select a material that suits your part’s function and requirements.
- Find a CNC Service Provider: Partner with a reputable CNC machining service to bring your design to life.
- Prototype and Test: Create a prototype to test the design and make any necessary adjustments.
- Move to Production: Once satisfied, proceed with full-scale production.
Final Thoughts
CNC machining is a powerful tool that combines precision, efficiency, and versatility. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, understanding the basics can help you make informed decisions and bring your ideas to fruition.
If you’re ready to explore CNC machining further or have a project in mind, feel free to reach out to us. We’re here to help you every step of the way!